8. (b) Health is the outcome of interaction between physical setting, cultural traits and ecological connection. Explain. 15 Marks (PYQ/2024)
Answer:
Introduction
Health is not merely the absence of disease; it is a holistic state influenced by the physical setting (such as climate, urban design, and environmental quality), cultural traits (including traditional practices, diet, and social norms), and the broader ecological connection (the relationship between humans and nature). In India, diverse geographies, rich cultural heritages, and varied ecosystems interact in complex ways to shape health outcomes. Understanding these interconnections is essential for developing effective public health strategies.

Models
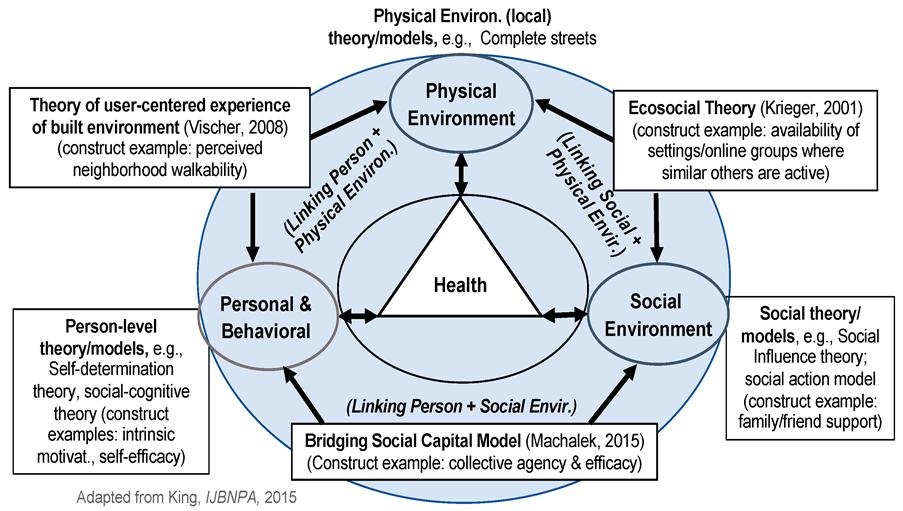
Social-Ecological Model
- Overview: The Social-Ecological Model, formulated by Urie Bronfenbrenner, demonstrates that health results from multiple layers of influence—from individual and interpersonal factors to community, institutional, and environmental levels.
- Key Insight: This model highlights how physical settings (urban planning, pollution) and ecological factors (biodiversity, natural resources) interact with cultural practices (dietary traditions, health beliefs) to impact individual and community health.
- Application: For instance, urban areas with green spaces and low pollution combined with cultural emphasis on outdoor activities tend to show better health outcomes.
GIS-Based Health Impact Models
- Overview: Geographic Information Systems (GIS) are used to map environmental risk factors and health indicators, illustrating the spatial relationship between physical settings and disease patterns.
- Key Insight: These models allow policymakers to pinpoint areas with hazardous environmental exposures and target interventions, thereby proving essential in planning healthy urban and rural spaces.
- Source: Reports by WHO and the Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR).
Theories
Social Determinants of Health Theory
- Overview: Developed by Dahlgren & Whitehead (1991), this theory argues that health is determined by a range of social, economic, and environmental factors.
- Key Insight: Cultural traits—such as traditional diets, social cohesion, and indigenous health practices—combine with good ecological connections (like access to clean water and air) to positively influence health outcomes.
Cultural Epidemiology
- Overview: This theory examines how cultural beliefs and practices influence the distribution and experience of health and disease.
- Key Insight: In India, cultural practices (e.g., using natural remedies or practicing yoga) contribute to holistic health and resilience, illustrating how cultural traits are interwoven with public health.
Laws
National Health Policy (2017) & Environmental Legislation
- Overview: The National Health Policy 2017 emphasizes preventive health and recognizes the role of environmental factors in public health strategies.
- Supporting Legislation: The Environment (Protection) Act, 1986 and various state-level regulations set standards for air and water quality, directly impacting the physical setting.
- Key Insight: These laws ensure that both environmental quality and cultural contexts (such as promoting traditional, healthy lifestyles) are considered in public health planning.
- Source: Ministry of Health and Family Welfare, Government of India; Official Gazette.
Perspectives
Sustainable Development Perspective
- Overview: From the Brundtland Commission’s perspective, sustainable development requires balancing economic growth with environmental protection and social equity.
- Key Insight: Integrating ecological sustainability with cultural preservation can lead to improved long-term health outcomes.
Political Economy Perspective
- Overview: Immanuel Wallerstein and others emphasize that power dynamics and resource allocation significantly affect health.
- Key Insight: In India, disparities in access to clean environments and culturally sensitive health services explain some of the regional health differences, underscoring the need for equitable policies.
Case Studies
Case Study 1: Air Pollution and Health in Delhi
- Overview: Delhi—a densely populated urban center—has faced severe air pollution issues impacting public health.
- Data & Impact: The Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB) reports average PM2.5 levels in Delhi of around 113 µg/m³, significantly higher than the WHO guideline of 25 µg/m³. Increased rates of respiratory diseases and cardiovascular conditions have been documented.
- Key Cultural Aspect: Despite rising pollution, traditional practices like the use of herbal remedies persist, which form part of the community’s cultural traits in managing health.
- Source: CPCB; WHO Global Urban Ambient Air Quality Database.
Case Study 2: Kerala’s Holistic Health Outcomes
- Overview: Kerala is renowned for its excellent health indicators, including high life expectancy and low infant mortality rates.
- Data & Impact: The National Family Health Survey (NFHS-4, 2015-16) reports a life expectancy in Kerala of over 75 years, compared to the national average of approximately 69 years. A strong ecological connection due to abundant water bodies and lush greenery, along with culturally ingrained practices such as Ayurveda and community-based health initiatives, contribute significantly.
- Key Insight: The integration of physical settings that promote green spaces and cultural practices focused on preventive health has yielded superior public health outcomes.
- Source: National Family Health Survey (NFHS-4); Economic Survey of Kerala.
Conclusion
Health in India is the cumulative outcome of dynamic interactions among the physical setting, cultural traits, and ecological connection. Using models such as the Social-Ecological Model and GIS-based analysis, alongside theories of Social Determinants of Health and Cultural Epidemiology, and backed by robust legal frameworks, we can see how integrated efforts promote holistic health outcomes.
Tag:cultural traits and ecological connection, Geography Case Study, Geography Optional, geography optional case study, Geography Optional Pyq, geography optional pyq 2024, Health and ecological connection, health is outcome of interaction between physical setting, human geography, Indian Geography, models theories laws and perspective in geography