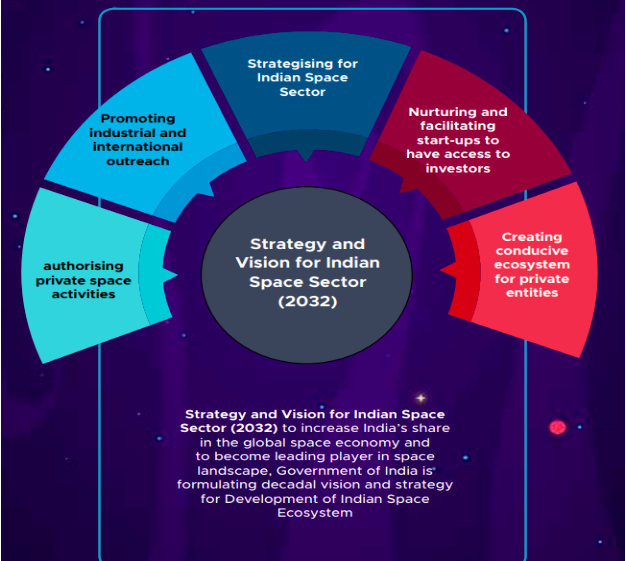
2. (b) The Indian Space Policy, 2023 supports the commercial presence in space. In what ways will it benefit the socio-economic development and security of India? 15Marks (PYQ/2024)
Answer:
1. Introduction
The Indian Space Policy, 2023 marks a strategic shift by embracing private sector participation alongside ISRO-led initiatives. The policy envisions a vibrant commercial space industry that will not only drive innovation and economic growth but also strengthen India’s national security apparatus. By leveraging advanced technologies, fostering strategic partnerships, and opening up new markets, the policy is positioned to create significant spillover effects across various sectors of the economy and defense. This approach is underpinned by established models and theories from innovation economics, cluster theory, spatial networks, and dual-use technology frameworks, alongside global and domestic legal instruments that regulate space activities.

Image source: PIB
2. Socio-Economic Development Benefits
Economic Growth and Employment
- Cluster Theory & Innovation Economies: Drawing on Porter’s Cluster Theory, the policy is expected to catalyze the formation of high-technology clusters. When private space enterprises, startups, and research institutions are geographically co-located, they create innovation hubs that stimulate knowledge spillovers, attract venture capital, and generate high-skilled jobs. This concentrated growth can be compared to “growth centres” in urban economics where specialized industries catalyze regional development.
- Diffusion of Innovation and Spillover Models: The Diffusion of Innovation model (Rogers) explains how new technologies spread through networks. In the context of the space industry, innovations such as satellite communications, remote sensing, and Earth observation technologies will quickly disseminate across sectors like agriculture, disaster management, and urban planning. These technologies enhance service delivery and improve productivity across the country.
Enhanced Public Services and Rural Connectivity
- Spatial Diffusion and Network Theories: Using spatial diffusion models and gravity principles, an expanded satellite constellation can reduce the digital divide by improving connectivity in remote and rural areas. Enhanced connectivity is critical for e-governance, telemedicine, and digital financial services, directly contributing to a more inclusive socio-economic landscape.
- Knowledge Spillover and Economic Multipliers: By fostering partnerships between private enterprises and academic institutions, the policy is poised to revolutionize education, research, and development. These linkages drive human and intellectual capital accumulation, providing a long-term boost to India’s innovation-driven economy.
Legal and Policy Frameworks
- Commercial Space Activities Bill (Proposed): India’s ongoing efforts to draft and implement a Commercial Space Activities Bill signal strong regulatory support. This legal framework will provide clear guidelines for private participation, risk management, and dispute resolution, thereby reducing uncertainties for investors and fostering a predictable business environment.
- International Space Law – Outer Space Treaty (1967): As a signatory to the Outer Space Treaty, India adheres to global norms ensuring that space activities are conducted peacefully and for the benefit of all countries. The policy aligns with these principles while promoting commercialization, ensuring responsible and sustainable use of outer space.
3. National Security Benefits
Strengthening Strategic Autonomy
- Dual-Use Technology Frameworks: Many space technologies possess dual civilian and military applications. Enhanced satellite surveillance, secure communication networks, and improved navigation systems are critical for national defense. Dual-use frameworks underscore that investments in commercial space industries can simultaneously enhance security capabilities.
- Network Theory and Redundancy Models: The concept of network resilience suggests that diversified, interconnected nodes (i.e., multiple satellite platforms) reduce vulnerability. A distributed space asset portfolio ensures that no single point of failure can compromise national security, reinforcing India’s strategic autonomy in an increasingly contested space domain.
Geopolitical Leverage and Regional Influence
- Global Trade and Diplomacy Models: By establishing itself as a major player in the global space market, India can leverage soft power through technology exports and international collaborations. This economic diplomacy strengthens geopolitical ties and enhances India’s position in strategic multilateral forums.
- Economic Security and Strategic Investments: Economic security models highlight that robust investments in high-technology sectors provide the backbone for national defense. The policy’s emphasis on private-public partnerships and innovation clusters creates a dynamic ecosystem that contributes both to prosperity and secure defense readiness.
4. Perspectives, Models, and Legal Instruments
- Models & Theories:
- Cluster Theory (Porter) and Diffusion of Innovation (Rogers) drive socio-economic benefits.
- Dual-Use Technology and Network Resilience Models underpin the national security benefits.
- Spatial Diffusion and Gravity Models help optimize the placement and connectivity of technological assets.
- Perspectives:
- Economic Perspective: Emphasizes market efficiency, employment multipliers, and global competitiveness.
- Security Perspective: Focuses on strategic autonomy, border surveillance, and robust defense networks.
- Social Perspective: Highlights improved public services, digital inclusion, and rural connectivity.
- Legal Frameworks and Laws:
- Outer Space Treaty (1967): Establishes the legal principles for peaceful space exploration.
- Proposed Commercial Space Activities Bill: Provides domestic legal clarity for private sector engagement.
- IT Act and Cyber Laws: Ensure secure data transmission and satellite communication networks.
Conclusion
The Indian Space Policy, 2023, by fostering a robust commercial space ecosystem, is set to drive significant socio-economic growth and enhance national security. By leveraging models such as Cluster Theory, Diffusion of Innovation, Dual-Use Technology frameworks, and Network Resilience models, the policy creates well-integrated linkages between commercial ambitions and strategic imperatives. Supported by a coherent legal framework that includes international space law and proposed domestic regulations, the policy ensures that India remains at the forefront of technology-driven progress, economic prosperity, and national security in the global arena.
Tag:commerical presence in space, Geography Case Study, Geography Optional, geography optional case study, Geography Optional Pyq, geography optional pyq 2024, human geography, Indian space policy, models theories laws and perspective in geography, socio-economic development and security of India and Indian Space Policy 2023