Answer:Introduction The morphology of Indian towns reflects a historical evolution from organic settlements to colonial urban structures and, eventually, modern planned cities. Early towns developed around forts, markets, and religious centers, fostering dense, irregular street patterns. Colonial interventions brought cantonments …
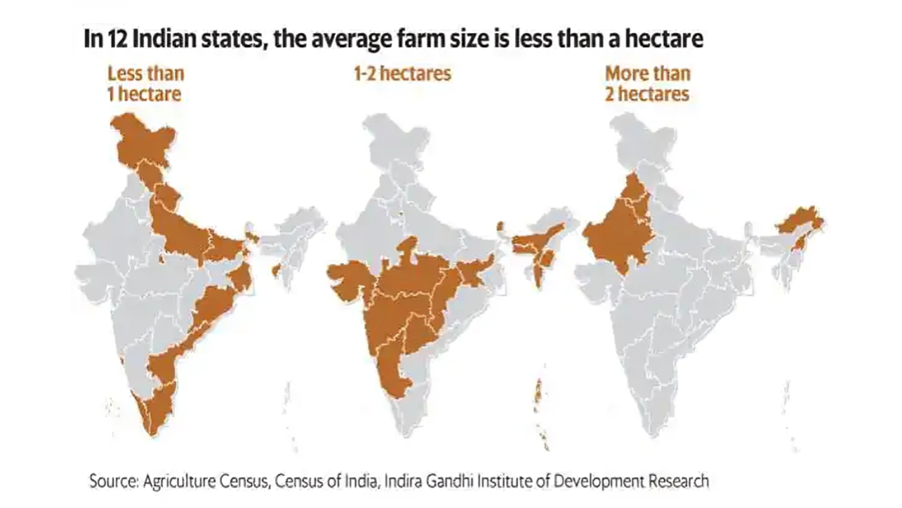
Answer: Introduction In India, small and fragmented landholdings are a hallmark of rural agriculture. Over 86% of Indian farmers are classified as small and marginal, with the average operational holding shrinking from approximately 2.3 hectares in 1970–71 to about 1.08 …
Answer: Introduction The 73rd Constitutional Amendment Act, 1992 is a watershed in Indian democracy that empowered rural areas by providing constitutional status to Panchayati Raj Institutions (PRIs). This landmark reform established a three-tier system of local government, devolved functions, finances, …
Answer: Introduction India has emerged as a powerful player in global governance by actively engaging in multilateral forums such as the G-7, G-20, BRICS, Quad, and regional gatherings like the Voice of Global South Summit. By taking proactive stands during …
Answer: The Jal Shakti Abhiyan: Catch the Rain 2024 campaign aims to enhance water conservation across India with the theme “Nari Shakti se Jal Shakti”, emphasizing women’s role in sustainable water management. Implemented from March to November 2024, it focuses …
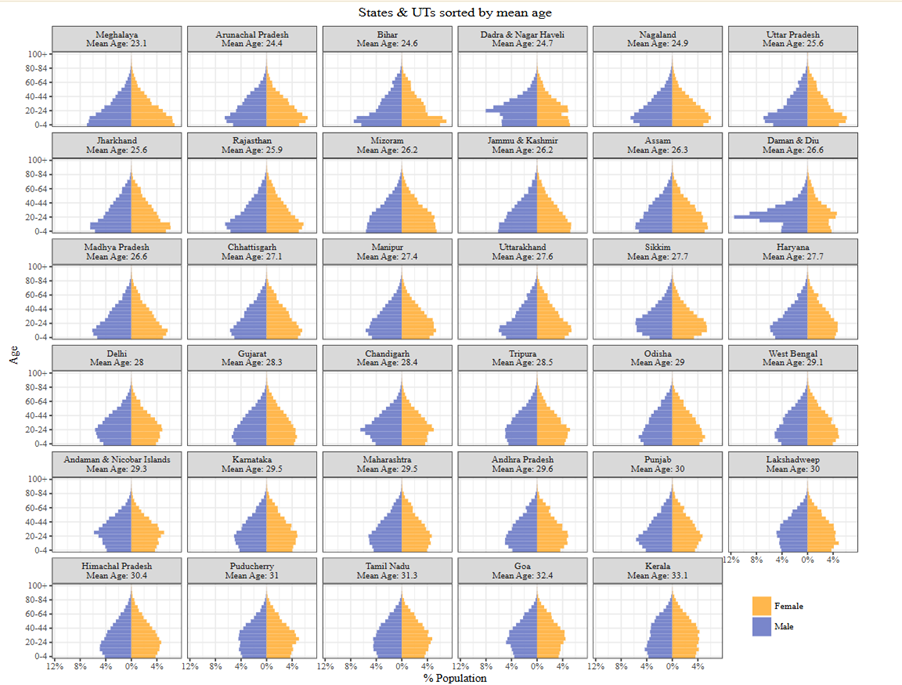
Answer: Introduction The cultural diversity of India—from deeply entrenched patriarchal practices in some northern states to relatively progressive gender norms in southern regions—profoundly influences the sex structure (the ratio of females to males) and the age structure (the distribution of …
Answer: Introduction Industrial waste in India is highly diversified, spanning hazardous chemical residues, solid wastes from manufacturing, by-products from textile, tannery, and food processing industries, and electronic waste. Such industrial by-products offer substantial potentials—including resource recovery, energy generation, and employment …
Answer: Introduction Seaports have long been recognized as vital growth poles that drive regional economic development. In India, the strategic location of seaports along the extensive coastline has catalyzed industrialization, enhanced trade, and spurred infrastructure investments in adjacent regions. The …
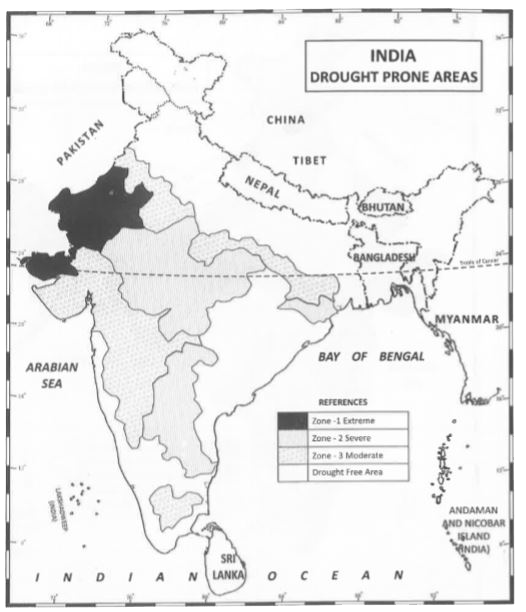
Answer: Introduction Drought‐prone areas in India—such as regions in Bundelkhand, Marathwada, and parts of Rajasthan—suffer from low and erratic rainfall (often below 750–1000 mm annually) and poor water availability, which severely impact agriculture and livelihoods. In response, the government and …
Answer: Introduction Indian agriculture—traditionally labor‐intensive and reliant on conventional methods—is undergoing a profound transformation through the adoption of modern technology. With innovations spanning precision farming, Internet of Things (IoT), Artificial Intelligence (AI), and drones, technology has played a transitional role …