Q4. (a) How is carbon neutrality essential for future environmental conservation? Describe various efforts taken by nations in this regard. 20 Marks (PYQ/2024)
Answer:
Introduction
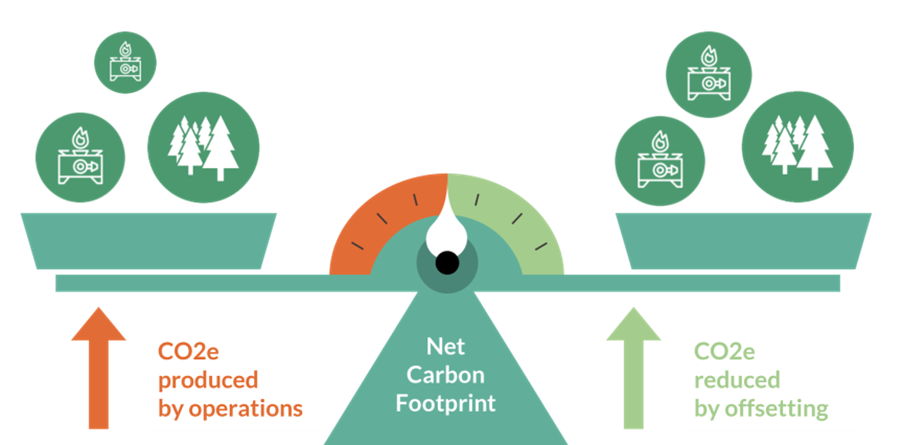
Carbon neutrality—achieving a balance between emitted and absorbed carbon dioxide—is critical for mitigating climate change and ensuring environmental sustainability. As global temperatures rise, extreme weather events become more frequent, and ecosystems face unprecedented stress, reducing greenhouse gas emissions is not merely an environmental imperative; it is central to safeguarding human health, biodiversity, and the Earth’s natural systems.

The Significance of Carbon Neutrality
- Mitigation of Climate Change: By achieving net-zero emissions, nations can slow global warming, stabilise weather patterns, and reduce the risks associated with sea level rise and natural disasters.
- Biodiversity and Ecosystem Health: Lowering carbon footprints helps preserve habitats, maintain ecosystem services, and support species resilience against rapid climate shifts.
- Socio-Economic Benefits: Transitioning to renewable energy sources creates green jobs, enhances energy security, and reduces reliance on fossil fuels, leading to sustainable economic growth.
Theoretical Framework and Perspectives
- Sustainable Development and the Precautionary Principle: Carbon neutrality aligns with the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) and embodies the precautionary approach, ensuring that human progress does not come at the expense of future environmental integrity.
- Systems Theory: Recognizing that ecosystems are interconnected, reducing carbon emissions has systemic benefits—improving air quality, water cycles, and soil health—which in turn support human well-being.
- Environmental Justice: Achieving carbon neutrality can help address disparities; vulnerable communities often bear the brunt of pollution and climate-related impacts, so a cleaner, greener approach benefits all.
Global Efforts Toward Carbon Neutrality
- European Union (EU) – The European Green Deal: The EU has set an ambitious target to become carbon neutral by 2050 through measures that include transitioning to renewable energy, supporting sustainable agriculture, and enhancing energy efficiency.
- United Kingdom: The UK is committed to a net-zero target by 2050, rolling out strategies to phase out fossil fuels, invest in electric public transport, and foster green industries through supportive policy frameworks.
- United States: Under recent administrations, the U.S. has re-engaged with international climate agreements and initiated policies to cut emissions, promote renewable energy innovations, and stimulate carbon capture research, with a goal of achieving net-zero emissions by mid-century.
- China: As the world’s largest emitter, China has pledged to reach carbon neutrality by 2060, simultaneously investing heavily in solar, wind, and nuclear power as well as pioneering carbon sequestration projects.
- Other Initiatives: Countries like Japan, South Korea, and New Zealand are crafting comprehensive energy transition policies, while many developing nations are leveraging international funding and technology transfer to support green infrastructure.
Conclusion
Carbon neutrality is essential for preserving the planet’s ecological balance and ensuring sustainable human development. Global efforts—ranging from the EU’s Green Deal to China’s pledge—demonstrate that coordinated policy, advanced technology, and visionary leadership form the backbone of a strategy aimed at safeguarding the environment for future generations. Embracing carbon neutrality not only mitigates climate change but also fosters a healthier, more resilient world for all.