Case Study 1: Radical Geography and Social Justice – Housing Inequality in the United States Principles of Radical Geography: Theorists Behind the Principles: Models/Theories/Laws: Recent Data: Spatial Variation: Temporal Variation: Insight: Radical geography validates social justice models, emphasizing the role …
Case Study 1: Regional Synthesis in the Indo-Gangetic Plains – Agricultural and Economic Integration Principles of Regional Synthesis: Theorists Behind the Principles: Models/Theories/Laws: Recent Data: Spatial Variation: Temporal Variation: Insight: Regional synthesis in the Indo-Gangetic Plains validates economic geography models, …
Case Study 1: Soil Profile Development in the Indo-Gangetic Plains Geographical Thought & Perspectives: Models/Theories/Laws: Recent Data: Spatial Variation: Temporal Variation: Insight: Soil profile development in the Indo-Gangetic Plains validates pedogenesis models, emphasizing the role of climate and hydrology in …
Case Study 1: Gulf Stream Slowdown and Its Impact on European Climate Geographical Thought & Perspectives: Models/Theories/Laws: Recent Data: Spatial Variation: Temporal Variation: Insight: Gulf Stream slowdown validates ocean circulation models, emphasizing the role of climate change in altering global …
Case Study 1: Formation of the Himalayas Case Study 2: Deccan Traps and the Breakup of Gondwana
Answer: Introduction India’s urban centers have witnessed exponential growth over recent decades, leading to persistent problems such as traffic congestion, air pollution, and inefficient public transport. In response, the country has developed various regional rapid transit systems—including Metro Rail, Bus …
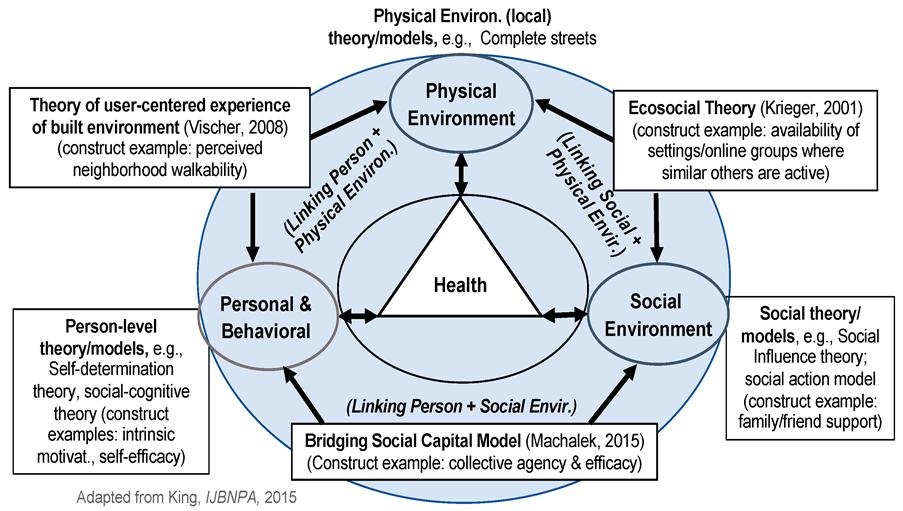
Answer: Introduction Health is not merely the absence of disease; it is a holistic state influenced by the physical setting (such as climate, urban design, and environmental quality), cultural traits (including traditional practices, diet, and social norms), and the broader …
Answer:Introduction The morphology of Indian towns reflects a historical evolution from organic settlements to colonial urban structures and, eventually, modern planned cities. Early towns developed around forts, markets, and religious centers, fostering dense, irregular street patterns. Colonial interventions brought cantonments …
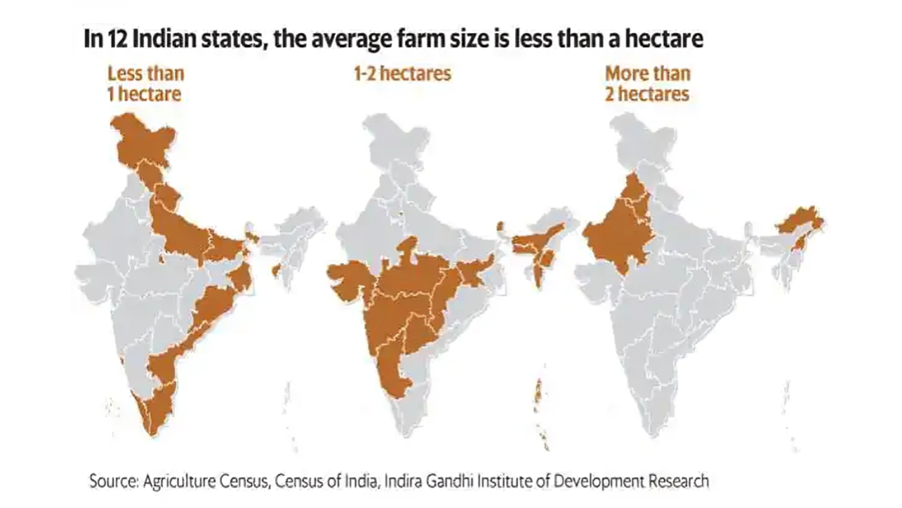
Answer: Introduction In India, small and fragmented landholdings are a hallmark of rural agriculture. Over 86% of Indian farmers are classified as small and marginal, with the average operational holding shrinking from approximately 2.3 hectares in 1970–71 to about 1.08 …
Answer: Introduction The 73rd Constitutional Amendment Act, 1992 is a watershed in Indian democracy that empowered rural areas by providing constitutional status to Panchayati Raj Institutions (PRIs). This landmark reform established a three-tier system of local government, devolved functions, finances, …