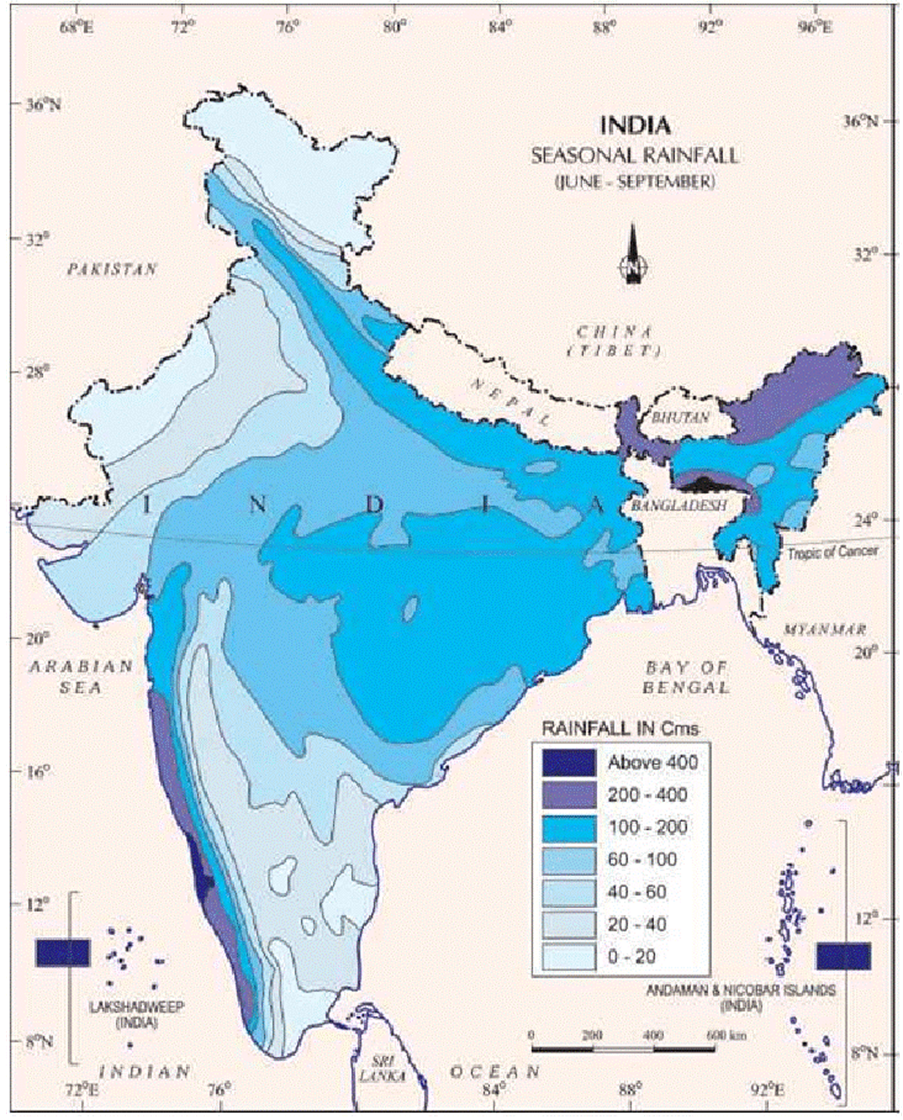
Answer: Introduction High annual rainfall in India is not uniformly distributed. Instead, it is strongly influenced by various geographic factors such as topography, altitude, proximity to water bodies, and regional climate patterns. For instance, the Western Ghats and the Northeast …
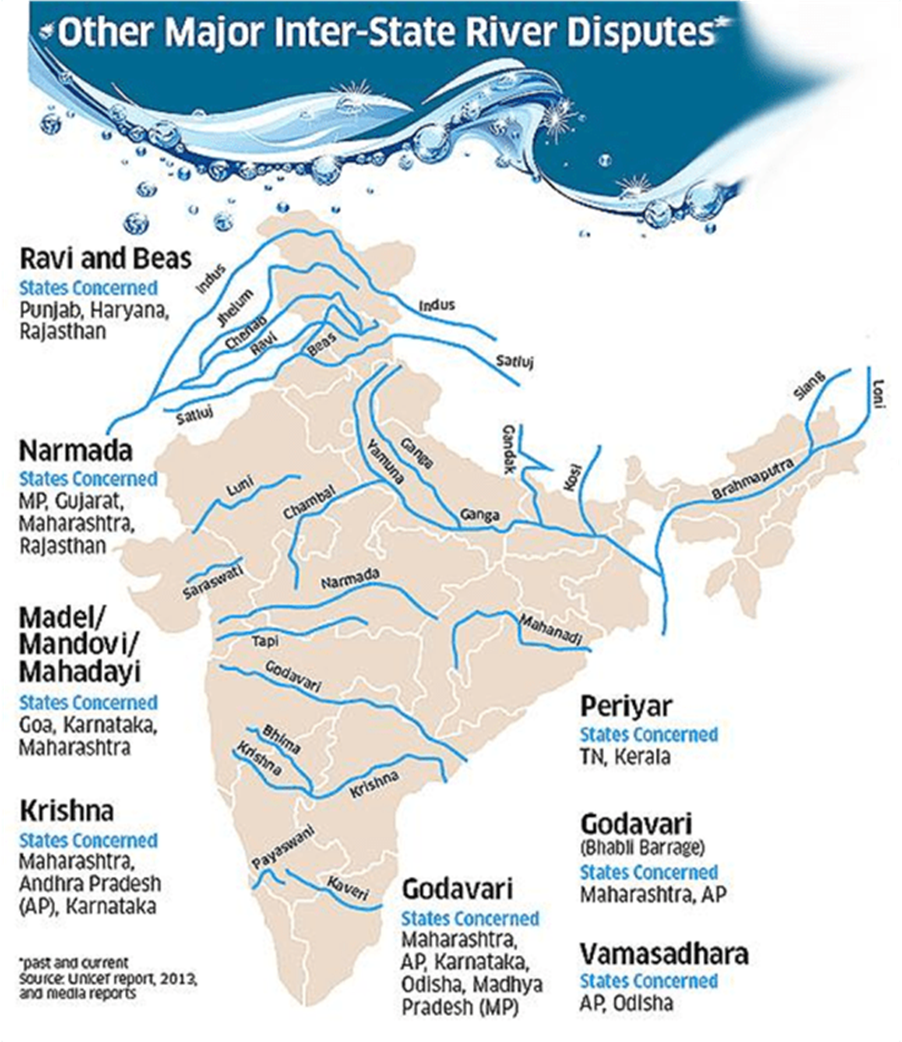
Answer:Introduction Water scarcity is one of the most daunting challenges in India, leading to disputes and conflicts among states and communities. Rapid population growth, climate change, uneven rainfall, and over-extraction of groundwater exacerbate the problem. To address these issues efficiently, …
Answer: Introduction Tribal areas in India, home to approximately 8.6% of the population (Census of India, 2011), continue to experience underdevelopment despite a long history of targeted development programmes such as the Tribal Sub-Plan, Integrated Tribal Development Programme (ITDP), and …
Answer: Introduction Migration in India is a clear manifestation of regional disparities. Economic opportunities, differences in public services, educational facilities, and infrastructural development have led people to move from less developed regions to prosperous urban centers. This migration produces distinct …
Introduction Domestic tourism in India leverages its extensive cultural, historical, and ecological resources, making it a crucial driver for socio-economic development. India’s distinct regional offerings—from its ancient heritage sites to diverse natural landscapes—coupled with supportive government policies and emerging market …
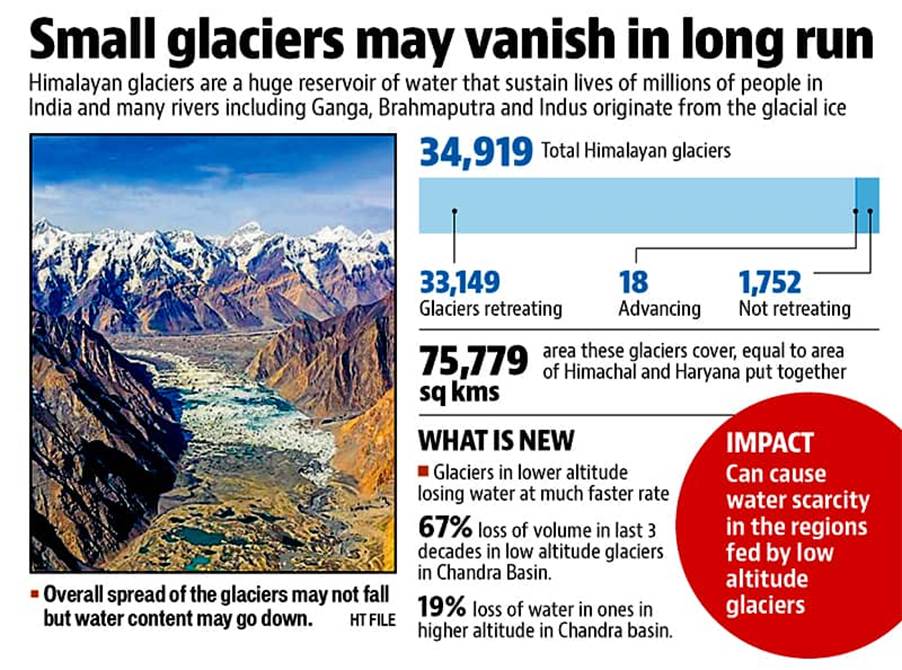
Answer: Introduction Glaciers in India—primarily in the Himalayan region—are critical components of the cryosphere, influencing regional hydrology and water security. These glaciers vary in type—from valley glaciers to debris-covered and hanging glaciers—and exhibit complex behaviors when viewed as dynamic systems. …
Answer: Introduction India is marked by wide-ranging regional disparities in economic development—a phenomenon shaped by historical legacies, geographic diversity, policy choices, and infrastructural investments. While certain regions, such as urban centers and coastal states, have emerged as vibrant economic cores, …
Answer: Introduction Conurbations are vast, continuously built-up urban areas formed by the merging or clustering of adjacent cities and towns. In India, rapid urbanization driven by economic opportunities, rural-to-urban migration, and infrastructural development has resulted in the formation of sprawling …
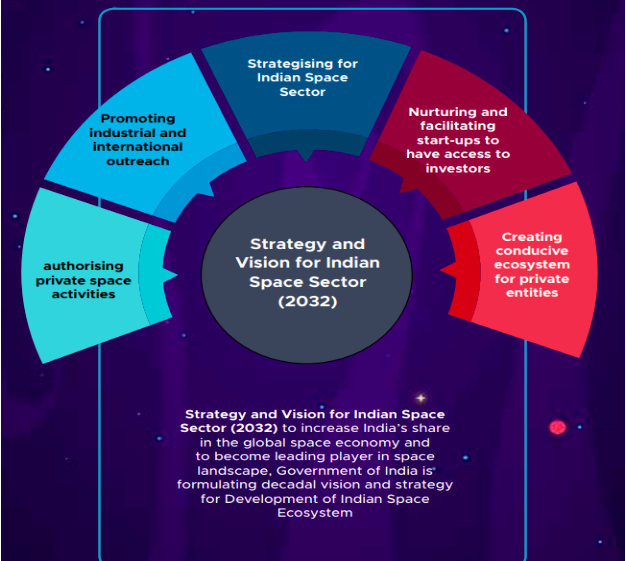
Answer: 1. Introduction The Indian Space Policy, 2023 marks a strategic shift by embracing private sector participation alongside ISRO-led initiatives. The policy envisions a vibrant commercial space industry that will not only drive innovation and economic growth but also strengthen …
Answer: Introduction: Agricultural prosperity in India is shaped by institutional factors such as government policies, financial systems, research institutions, and cooperative movements. These factors influence productivity, market stability, and rural incomes. Theoretical perspectives, models, and legal frameworks provide a structured …